Global advertising is set to pass the $1trn mark in 2024, following a year of extraordinary 10% growth – with retail media, social media and search leading the charge.
According to the latest figures from WARC, global advertising spend is on course to grow 10.7% this year to a total of $1.08trn – the strongest growth rate in six years and the largest absolute rise on record if the post-Covid.
And the growth has been across the board, with all forms of advertising – even print and linear TV – making significant gains.
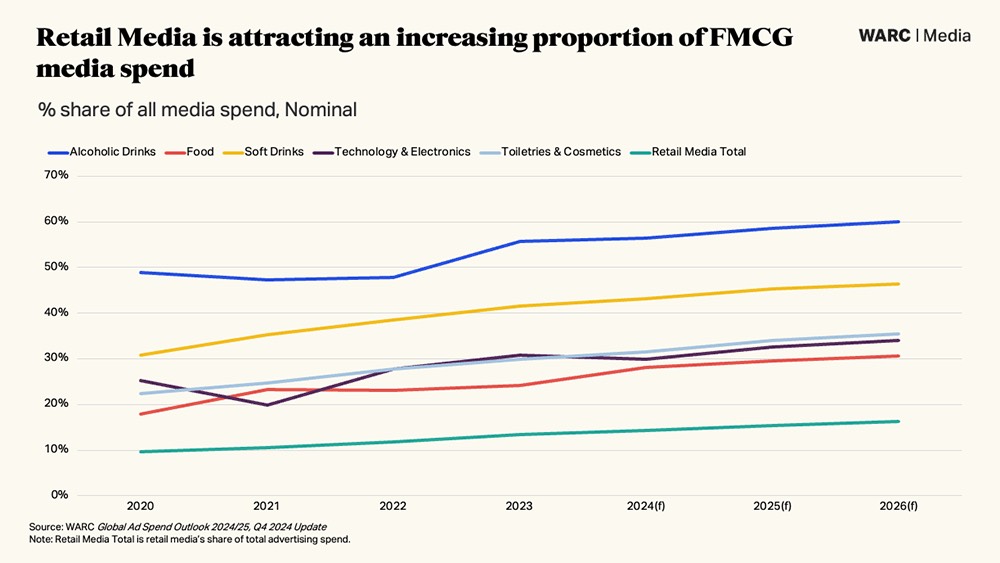
Retail media has seen 18% growth year-on-year between 2023 and 2024, topping $154.8bn for the year globally. It is on course to grow 14% next year to $177bn and then pass the $200bn mark by the end of 2026.
Happy holidays?
Advertisers the world over are expected to spend $299.2bn during the final quarter of the year, well over half of which will be spent during the holiday season. This represents a 10.2% rise from the previous year, up marginally (+0.2pp) from our August forecast.
The fourth quarter is crucial for retailers, typically accounting for over 30% of annual ad spend within the sector which represents the intense battle for consumer salience and share of wallet each year.
Retailers will spend $45.6bn on advertising during Q4 2024, up 5.0% compared to last year. TV is set to attract 15.9% of this spend, at $6.8bn, with nearing a quarter (23.3%) of this – $1.6bn – spent on ads delivered via connected TVs (CTV) so as to leverage the additional targeting capabilities these devices can afford advertisers.
Advertising on retail media platforms is also set to peak during the fourth quarter as brands vie to reach consumers close to the point of purchase. Globally, retail media spend is forecast to rise 16.4% in Q4 2024 to a total of $46.2bn – a new high. Amazon alone is expected to net $16.9bn from advertisers at this time, up 18.0% from the previous year.
The technology and electronics sector is expected to spend most in online retail media environments during the fourth quarter, with an anticipated total of $7.2bn up 18.7% from last year. For context, this is over three times more than the sector spends on TV.
It’s also a big time of year for fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) brands, with the alcoholic drinks (+13.5% to $3.9bn), cosmetics (+13.8% to $5.2bn), food (+19.4% to $5.4bn) and soft drinks (+22.0% to $4.5bn) sectors all increasing retail media spend and allocating an increasing share of their ad budgets to online retail platforms this year.
In context
While retail media has made a significant contribution to overall ad revenues, it is just part of the mix and, in context, still has some way to go to compete with the mainstream ad channels.
Social media is the largest individual sector within pure play internet – and the largest advertising medium of all by extension – with a total of $252.7bn this year equivalent to 23.5% of the global ad market. Prospects for the social market have been revised upwards this year to +19.3%, owing mostly to stronger-than expected results for Facebook, Instagram and TikTok over the first nine months of the year.
Building upon a solid performance for legacy media, pure play internet, which encompasses advertising revenue among online-only businesses such as Alphabet, Amazon and Meta, is poised to grow by 14.1% to a total of $741.4bn – over two thirds (68.8%) of all ad spend.
One in five dollars (22.1%) spent on advertising outside of China is paid to Google for its search services. Further, at an expected $197.7bn in 2024 (+13.0% year-on-year), Google alone accounts for 90.1% of all search advertising (excluding China). These commanding shares are similar in the US, leading the Department of Justice (DOJ) to rule last week that Google has an effective monopoly on the search market.
The court believes that Google also uses its search dominance to inflate the cost per click (up by approximately 7.5% this year) and maintain superior targeting, effectively blocking competitors from offering viable alternatives.
Outcomes from the ruling range from Google ceasing payments to handset manufactures and others for default preference – at a cost of approximately $30bn per annum – to the selling off of its Chrome business to a third party.
One potential suitor – Bing – still struggles with adoption and advertiser investment despite Microsoft’s $100bn investment, accounting for just 5.9% of search spend outside of China. Bing’s ad revenues are expected to be up just 5.1% this year – compared to a rise of 11.9% for total search and 13.0% for Google – to a total of $12.9bn.
Apple already makes $5.1bn from search ads, mostly via its app store, per Omdia Advertising Intelligence estimates, and could create its own search engine given its financial and distribution resources. The device manufacturer may hesitate to proceed, however, due to the high costs associated with maintaining a search business aside a general strategic misalignment. A leftfield entrant – perhaps Elon Musk’s X on the lookout for new revenue streams after losing $5.9bn in ad revenue since its 2022 takeover – may materialise, but on the whole natural successors to Google remain unclear.
With the ongoing uncertainty around the practicalities of the DOJ ruling, and the probability that Google will appeal it vigorously in the coming months, WARC is maintaining its growth forecast of +9.0% next year and +7.0% in 2026 for the company while the situation develops, leaving a potential $231bn ad business and $32.9bn of growth in the balance over the next two years.